Mustang PRIDE Teacher Webpage
-
What is PBIS?
Positive Behavioral Interventions and Supports (PBIS) is an evidence-based three-tiered framework for improving and integrating all of the data, systems, and practices affecting student outcomes every day. It is a way to support everyone – especially students with disabilities – to create the kinds of schools where all students are successful.
Three Tiers of Support
PBIS is a multi-tiered framework – three tiers, to be exact. Each tier aligns to the type of support students need. These three tiers are:
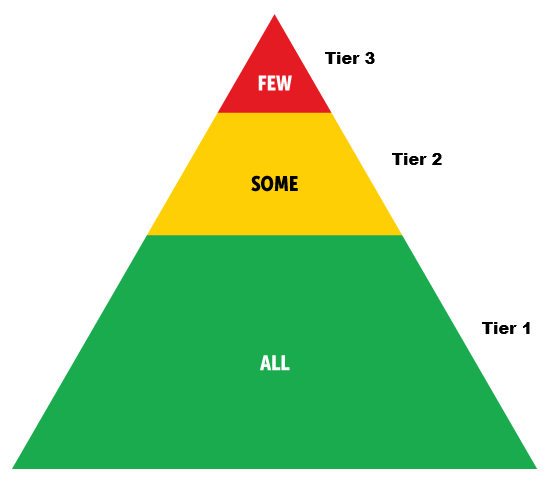
Tier 1: Universal Prevention (All students)
Tier 1 systems, data, and practices impact everyone across all settings. They establish the foundation for delivering regular, proactive support and preventing unwanted behaviors. Tier 1 emphasizes prosocial skills and expectations by teaching and acknowledging appropriate student behavior.
Tier 1 foundational systems include:
- An established leadership team
- Regular meetings
- A commitment statement for establishing a positive school-wide social culture
- On-going use of data for decision making
- Professional development plans
- Personnel evaluation plan
Tier 1 practices include:
- School-wide positive expectations and behaviors are taught
- Established classroom expectations aligned with school-wide expectations
- A continuum of procedures for encouraging expected behavior
- A continuum of procedures for discouraging problem behavior
- Procedures for encouraging school-family partnership
Tier 2: Targeted Prevention (Some=about 5% of students)
Tier 2 systems, data, and practices provide targeted support for students who are not successful with Tier 1 supports alone. The focus is on supporting students who are at risk for developing more serious problem behavior before those behaviors start. Tier 2 supports often involve group interventions with 10 or more students participating. The support at this level is more focused than Tier 1 and less intensive than Tier 3.
Tier 2 foundational systems include:
- An intervention team with a coordinator
- Behavioral expertise
- Fidelity and outcome data are collected
- A screening process to identify students needing Tier 2 support
- Access to training and technical assistance
Tier 2 practices include:
- Increased instruction and practice with self-regulation and social skills
- Increased adult supervision
- Increased opportunities for positive reinforcement
- Increased pre-corrections
- Increased focus on possible function of problem behaviors
- Increased access to academic supports
Tier 3: Intensive, Individualized Prevention (Few=about 3% of students)
At most schools, there are 1-5% of students for whom Tier 1 and Tier 2 supports have not connected. At Tier 3, these students receive more intensive, individualized support to improve their behavioral and academic outcomes. Tier 3 strategies work for students with developmental disabilities, autism, emotional and behavioral disorders, and students with no diagnostic label at all.
Tier 3 foundational systems include:
- A multi-disciplinary team
- Behavior support expertise
- Formal fidelity and outcome data are collected
Tier 3 practices include:
- Function-based assessments
- Wraparound supports
- Cultural and contextual fit

 CVUSD HOME
CVUSD HOME